注意
到末尾下载完整的示例代码。
示例:VAR(2) 过程
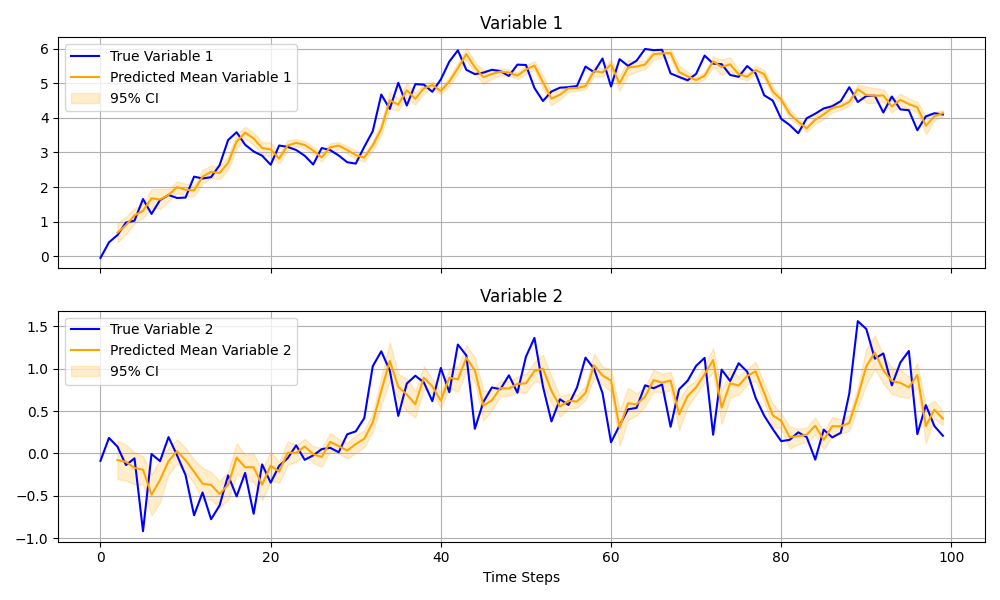
在本示例中,我们将演示如何实现向量自回归二阶过程 (VAR(2)) 并对其进行贝叶斯推断。VAR 模型在时间序列分析中被广泛应用,尤其适用于捕捉多个变量之间的动态关系。
对于包含 \(K\) 个变量的多元时间序列 \(y_t\),VAR(2) 过程定义为
\[y_t = c + \Phi_1 y_{t-1} + \Phi_2 y_{t-2} + \epsilon_t\]
这里,\(c\) 是一个常数向量,\(\Phi_1\) 和 \(\Phi_2\) 分别是滞后 1 和滞后 2 的系数矩阵,\(\epsilon_t\) 是一个零均值、协方差矩阵为 \(\Sigma\) 的高斯噪声项。
本示例使用 NumPyro 的 scan 工具来有效建模时间依赖性,避免显式的 Python 循环。
有关更通用的时间序列预测技术和示例,请参阅时间序列预测教程:https://num.pyro.org.cn/en/stable/tutorials/time_series_forecasting.html#Forecasting
参考
有关向量自回归模型的更多信息,请参阅:https://otexts.com/fpp2/VAR.html
import argparse
import os
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from jax import random
import jax.numpy as jnp
import numpyro
from numpyro.contrib.control_flow import scan
import numpyro.distributions as dist
def var2_scan(y):
T, K = y.shape # Number of time steps and number of variables
# Priors for constants and coefficients
c = numpyro.sample("c", dist.Normal(0, 1).expand([K])) # Constants vector of size K
Phi1 = numpyro.sample(
"Phi1", dist.Normal(0, 1).expand([K, K]).to_event(2)
) # Coefficients for lag 1
Phi2 = numpyro.sample(
"Phi2", dist.Normal(0, 1).expand([K, K]).to_event(2)
) # Coefficients for lag 2
# Priors for error terms
sigma = numpyro.sample("sigma", dist.HalfNormal(1.0).expand([K]).to_event(1))
L_omega = numpyro.sample(
"L_omega", dist.LKJCholesky(dimension=K, concentration=1.0)
)
L_Sigma = (
sigma[..., None] * L_omega
) # Alternative: jnp.einsum("...i,...ij->...ij", sigma, L_omega)
def transition(carry, t):
y_prev1, y_prev2, y_obs = carry # Previous two observations and observed data
m_t = c + jnp.dot(Phi1, y_prev1) + jnp.dot(Phi2, y_prev2) # Mean prediction
# Conditioned on observed y
y_t = numpyro.sample(
f"y_{t}",
dist.MultivariateNormal(loc=m_t, scale_tril=L_Sigma),
obs=y_obs[t],
)
new_carry = (y_t, y_prev1, y_obs)
return new_carry, m_t
# Initial carry: observations at time steps 1 and 0
init_carry = (y[1], y[0], y[2:])
# Time indices starting from time step 2
time_indices = jnp.arange(T - 2)
# Run the scan
_, mu = scan(transition, init_carry, time_indices)
# Store the mean trajectory as a deterministic variable
numpyro.deterministic("mu", mu)
def generate_var2_data(T, K, c, Phi1, Phi2, sigma):
"""
Generate time series data from a VAR(2) process.
Args:
T (int): Number of time steps.
K (int): Number of variables in the time series.
c (array): Constants (shape: (K,)).
Phi1 (array): Coefficients for lag 1 (shape: (K, K)).
Phi2 (array): Coefficients for lag 2 (shape: (K, K)).
sigma (array): Covariance matrix for the noise (shape: (K, K)).
Returns:
np.ndarray: Generated time series data (shape: (T, K)).
"""
# Initialize time series with random values
y = np.zeros((T, K))
y[:2] = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=np.zeros(K), cov=sigma, size=2)
# Generate the time series
for t in range(2, T):
y[t] = (
c
+ Phi1 @ y[t - 1]
+ Phi2 @ y[t - 2]
+ np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=np.zeros(K), cov=sigma)
)
return y
def run_inference(model, args, rng_key, y):
"""
Run MCMC inference for the given model.
Args:
model: The probabilistic model to infer.
args: Command-line arguments.
rng_key: PRNG key for randomness.
y: Observed time series data.
"""
start = time.time()
sampler = numpyro.infer.NUTS(model)
mcmc = numpyro.infer.MCMC(
sampler,
num_warmup=args.num_warmup,
num_samples=args.num_samples,
num_chains=args.num_chains,
progress_bar=False if "NUMPYRO_SPHINXBUILD" in os.environ else True,
)
mcmc.run(rng_key, y=y)
mcmc.print_summary()
print("\nMCMC elapsed time:", time.time() - start)
return mcmc.get_samples()
def main(args):
# Generate artificial dataset
T = args.num_data # Number of time steps
K = 2 # Number of variables
c_true = jnp.array([0.5, -0.3]) # Constants
Phi1_true = jnp.array([[0.7, 0.1], [0.2, 0.5]]) # Coefficients for lag 1
Phi2_true = jnp.array([[0.2, -0.1], [-0.1, 0.2]]) # Coefficients for lag 2
sigma_true = jnp.array([[0.1, 0.02], [0.02, 0.1]]) # Covariance matrix
rng_key = random.PRNGKey(0)
y = generate_var2_data(T, K, c_true, Phi1_true, Phi2_true, sigma_true)
# Perform inference
samples = run_inference(var2_scan, args, rng_key, y)
# Prediction
mean_prediction = samples["mu"].mean(axis=0)
lower_bound = jnp.percentile(samples["mu"], 2.5, axis=0) # 2.5th percentile
upper_bound = jnp.percentile(samples["mu"], 97.5, axis=0) # 97.5th percentile
# Plot results
fig, axes = plt.subplots(K, 1, figsize=(10, 6), sharex=True)
time_steps = jnp.arange(T)
for i in range(K):
# True values
axes[i].plot(time_steps, y[:, i], label=f"True Variable {i + 1}", color="blue")
# Posterior mean prediction
axes[i].plot(
time_steps[2:],
mean_prediction[:, i],
label=f"Predicted Mean Variable {i + 1}",
color="orange",
)
# 95% confidence interval
axes[i].fill_between(
time_steps[2:],
lower_bound[:, i],
upper_bound[:, i],
color="orange",
alpha=0.2,
label="95% CI",
)
axes[i].set_title(f"Variable {i + 1}")
axes[i].legend()
axes[i].grid(True)
plt.xlabel("Time Steps")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("var2.png")
if __name__ == "__main__":
assert numpyro.__version__.startswith("0.18.0")
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="VAR(2) example")
parser.add_argument("--num-data", nargs="?", default=100, type=int)
parser.add_argument("-n", "--num-samples", nargs="?", default=1000, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--num-warmup", nargs="?", default=1000, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--num-chains", nargs="?", default=1, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--device", default="cpu", type=str, help='use "cpu" or "gpu".')
args = parser.parse_args()
numpyro.set_platform(args.device)
numpyro.set_host_device_count(args.num_chains)
main(args)