注意
跳转至末尾以下载完整示例代码。
示例:高斯过程的希尔伯特空间近似。
本示例重现了 Aki Vehtari [1] 的优秀案例研究(最初使用 R 和 Stan 编写)中的模型。该案例研究使用近似高斯过程 [2] 对 1969 年至 1988 年美国每天的相对出生人数进行建模。希尔伯特空间近似比精确高斯过程快得多,因为它避免了协方差矩阵求逆的需求。
原始案例研究还强调了构建贝叶斯模型的迭代过程,这对于教学资源来说非常出色。然而,在此我们只重现包含所有组件(长期趋势、平滑的年度季节性、缓慢变化的星期效应、一年中的某一天效应以及特殊浮动日效应)的模型。
模型的不同组件被隔离到单独的函数中,以便它们可以在不同的上下文中轻松重用。为了将多个组件组合成一个生日模型,我们在此使用了 Numpyro 的 scope 处理器,它通过给组件的站点名称添加前缀来修改它们。通过这样做,我们避免了模型中站点名称的重复。遵循这种模式,使用此处提供的代码可以轻松构建 [1] 中的其他模型。
我们的模型在数学细节上有一些微小的差异,这些差异是我们为了使链条充分混合或便于实现而必须进行的。我们已经对模型不同的地方进行了注释。
周期核近似需要 jax 后端的 tensorflow-probability。有关安装说明,请参阅 <https://tensorflowcn.cn/probability/examples/TensorFlow_Probability_on_JAX>。
- 参考文献
Gelman, Vehtari, Simpson 等人 (2020),“贝叶斯工作流书籍 - 生日” <https://avehtari.github.io/casestudies/Birthdays/birthdays.html>。
Riutort-Mayol G, Bürkner PC, Andersen MR 等人 (2020),“用于概率编程的实用希尔伯特空间近似贝叶斯高斯过程”。
import argparse
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import jax
import jax.numpy as jnp
from tensorflow_probability.substrates import jax as tfp
import numpyro
from numpyro import deterministic, plate, sample
import numpyro.distributions as dist
from numpyro.handlers import scope
from numpyro.infer import MCMC, NUTS, init_to_median
# --- Data processing functions
def get_labour_days(dates):
"""
First monday of September
"""
is_september = dates.dt.month.eq(9)
is_monday = dates.dt.weekday.eq(0)
is_first_week = dates.dt.day.le(7)
is_labour_day = is_september & is_monday & is_first_week
is_day_after = is_labour_day.shift(fill_value=False)
return is_labour_day | is_day_after
def get_memorial_days(dates):
"""
Last monday of May
"""
is_may = dates.dt.month.eq(5)
is_monday = dates.dt.weekday.eq(0)
is_last_week = dates.dt.day.ge(25)
is_memorial_day = is_may & is_monday & is_last_week
is_day_after = is_memorial_day.shift(fill_value=False)
return is_memorial_day | is_day_after
def get_thanksgiving_days(dates):
"""
Third thursday of November
"""
is_november = dates.dt.month.eq(11)
is_thursday = dates.dt.weekday.eq(3)
is_third_week = dates.dt.day.between(22, 28)
is_thanksgiving = is_november & is_thursday & is_third_week
is_day_after = is_thanksgiving.shift(fill_value=False)
return is_thanksgiving | is_day_after
def get_floating_days_indicators(dates):
def encode(x):
return jnp.array(x.values, dtype=jnp.result_type(int))
return {
"labour_days_indicator": encode(get_labour_days(dates)),
"memorial_days_indicator": encode(get_memorial_days(dates)),
"thanksgiving_days_indicator": encode(get_thanksgiving_days(dates)),
}
def load_data():
URL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/avehtari/casestudies/master/Birthdays/data/births_usa_1969.csv"
data = pd.read_csv(URL, sep=",")
day0 = pd.to_datetime("31-Dec-1968")
dates = [day0 + pd.Timedelta(f"{i}d") for i in data["id"]]
data["date"] = dates
data["births_relative"] = data["births"] / data["births"].mean()
return data
def make_birthdays_data_dict(data):
x = data["id"].values
y = data["births_relative"].values
dates = data["date"]
xsd = jnp.array((x - x.mean()) / x.std())
ysd = jnp.array((y - y.mean()) / y.std())
day_of_week = jnp.array((data["day_of_week"] - 1).values)
day_of_year = jnp.array((data["day_of_year"] - 1).values)
floating_days = get_floating_days_indicators(dates)
period = 365.25
w0 = x.std() * (jnp.pi * 2 / period)
L = 1.5 * max(xsd)
M1 = 10
M2 = 10 # 20 in original case study
M3 = 5
return {
"x": xsd,
"day_of_week": day_of_week,
"day_of_year": day_of_year,
"w0": w0,
"L": L,
"M1": M1,
"M2": M2,
"M3": M3,
**floating_days,
"y": ysd,
}
# --- Modelling utility functions --- #
def spectral_density(w, alpha, length):
c = alpha * jnp.sqrt(2 * jnp.pi) * length
e = jnp.exp(-0.5 * (length**2) * (w**2))
return c * e
def diag_spectral_density(alpha, length, L, M):
sqrt_eigenvalues = jnp.arange(1, 1 + M) * jnp.pi / 2 / L
return spectral_density(sqrt_eigenvalues, alpha, length)
def eigenfunctions(x, L, M):
"""
The first `M` eigenfunctions of the laplacian operator in `[-L, L]`
evaluated at `x`. These are used for the approximation of the
squared exponential kernel.
"""
m1 = (jnp.pi / (2 * L)) * jnp.tile(L + x[:, None], M)
m2 = jnp.diag(jnp.linspace(1, M, num=M))
num = jnp.sin(m1 @ m2)
den = jnp.sqrt(L)
return num / den
def modified_bessel_first_kind(v, z):
v = jnp.asarray(v, dtype=float)
return jnp.exp(jnp.abs(z)) * tfp.math.bessel_ive(v, z)
def diag_spectral_density_periodic(alpha, length, M):
"""
Not actually a spectral density but these are used in the same
way. These are simply the first `M` coefficients of the low rank
approximation for the periodic kernel.
"""
a = length ** (-2)
J = jnp.arange(0, M)
c = jnp.where(J > 0, 2, 1)
q2 = (c * alpha**2 / jnp.exp(a)) * modified_bessel_first_kind(J, a)
return q2
def eigenfunctions_periodic(x, w0, M):
"""
Basis functions for the approximation of the periodic kernel.
"""
m1 = jnp.tile(w0 * x[:, None], M)
m2 = jnp.diag(jnp.arange(M, dtype=jnp.float32))
mw0x = m1 @ m2
cosines = jnp.cos(mw0x)
sines = jnp.sin(mw0x)
return cosines, sines
# --- Approximate Gaussian processes --- #
def approx_se_ncp(x, alpha, length, L, M):
"""
Hilbert space approximation for the squared
exponential kernel in the non-centered parametrisation.
"""
phi = eigenfunctions(x, L, M)
spd = jnp.sqrt(diag_spectral_density(alpha, length, L, M))
with plate("basis", M):
beta = sample("beta", dist.Normal(0, 1))
f = deterministic("f", phi @ (spd * beta))
return f
def approx_periodic_gp_ncp(x, alpha, length, w0, M):
"""
Low rank approximation for the periodic squared
exponential kernel in the non-centered parametrisation.
"""
q2 = diag_spectral_density_periodic(alpha, length, M)
cosines, sines = eigenfunctions_periodic(x, w0, M)
with plate("cos_basis", M):
beta_cos = sample("beta_cos", dist.Normal(0, 1))
with plate("sin_basis", M - 1):
beta_sin = sample("beta_sin", dist.Normal(0, 1))
# The first eigenfunction for the sine component
# is zero, so the first parameter wouldn't contribute to the approximation.
# We set it to zero to identify the model and avoid divergences.
zero = jnp.array([0.0])
beta_sin = jnp.concatenate((zero, beta_sin))
f = deterministic("f", cosines @ (q2 * beta_cos) + sines @ (q2 * beta_sin))
return f
# --- Components of the Birthdays model --- #
def trend_gp(x, L, M):
alpha = sample("alpha", dist.HalfNormal(1.0))
length = sample("length", dist.InverseGamma(10.0, 2.0))
f = approx_se_ncp(x, alpha, length, L, M)
return f
def year_gp(x, w0, M):
alpha = sample("alpha", dist.HalfNormal(1.0))
length = sample("length", dist.HalfNormal(0.2)) # scale=0.1 in original
f = approx_periodic_gp_ncp(x, alpha, length, w0, M)
return f
def weekday_effect(day_of_week):
with plate("plate_day_of_week", 6):
weekday = sample("_beta", dist.Normal(0, 1))
monday = jnp.array([-jnp.sum(weekday)]) # Monday = 0 in original
beta = deterministic("beta", jnp.concatenate((monday, weekday)))
return beta[day_of_week]
def yearday_effect(day_of_year):
slab_df = 50 # 100 in original case study
slab_scale = 2
scale_global = 0.1
tau = sample(
"tau", dist.HalfNormal(2 * scale_global)
) # Original uses half-t with 100df
c_aux = sample("c_aux", dist.InverseGamma(0.5 * slab_df, 0.5 * slab_df))
c = slab_scale * jnp.sqrt(c_aux)
# Jan 1st: Day 0
# Feb 29th: Day 59
# Dec 31st: Day 365
with plate("plate_day_of_year", 366):
lam = sample("lam", dist.HalfCauchy(scale=1))
lam_tilde = jnp.sqrt(c) * lam / jnp.sqrt(c + (tau * lam) ** 2)
beta = sample("beta", dist.Normal(loc=0, scale=tau * lam_tilde))
return beta[day_of_year]
def special_effect(indicator):
beta = sample("beta", dist.Normal(0, 1))
return beta * indicator
# --- Model --- #
def birthdays_model(
x,
day_of_week,
day_of_year,
memorial_days_indicator,
labour_days_indicator,
thanksgiving_days_indicator,
w0,
L,
M1,
M2,
M3,
y=None,
):
intercept = sample("intercept", dist.Normal(0, 1))
f1 = scope(trend_gp, "trend")(x, L, M1)
f2 = scope(year_gp, "year")(x, w0, M2)
g3 = scope(trend_gp, "week-trend")(
x, L, M3
) # length ~ lognormal(-1, 1) in original
weekday = scope(weekday_effect, "week")(day_of_week)
yearday = scope(yearday_effect, "day")(day_of_year)
# # --- special days
memorial = scope(special_effect, "memorial")(memorial_days_indicator)
labour = scope(special_effect, "labour")(labour_days_indicator)
thanksgiving = scope(special_effect, "thanksgiving")(thanksgiving_days_indicator)
day = yearday + memorial + labour + thanksgiving
# --- Combine components
f = deterministic("f", intercept + f1 + f2 + jnp.exp(g3) * weekday + day)
sigma = sample("sigma", dist.HalfNormal(0.5))
with plate("obs", x.shape[0]):
sample("y", dist.Normal(f, sigma), obs=y)
# --- plotting function --- #
DATA_STYLE = dict(marker=".", alpha=0.8, lw=0, label="data", c="lightgray")
MODEL_STYLE = dict(lw=2, color="k")
def plot_trend(data, samples, ax=None):
y = data["births_relative"]
x = data["date"]
fsd = samples["intercept"][:, None] + samples["trend/f"]
f = jnp.quantile(fsd * y.std() + y.mean(), 0.50, axis=0)
if ax is None:
ax = plt.gca()
ax.plot(x, y, **DATA_STYLE)
ax.plot(x, f, **MODEL_STYLE)
return ax
def plot_seasonality(data, samples, ax=None):
y = data["births_relative"]
sdev = y.std()
mean = y.mean()
baseline = (samples["intercept"][:, None] + samples["trend/f"]) * sdev
y_detrended = y - baseline.mean(0)
y_year_mean = y_detrended.groupby(data["day_of_year"]).mean()
x = y_year_mean.index
f_median = (
pd.DataFrame(samples["year/f"] * sdev + mean, columns=data["day_of_year"])
.melt(var_name="day_of_year")
.groupby("day_of_year")["value"]
.median()
)
if ax is None:
ax = plt.gca()
ax.plot(x, y_year_mean, **DATA_STYLE)
ax.plot(x, f_median, **MODEL_STYLE)
return ax
def plot_week(data, samples, ax=None):
if ax is None:
ax = plt.gca()
weekdays = ["Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
y = data["births_relative"]
x = data["day_of_week"] - 1
f = jnp.median(samples["week/beta"] * y.std() + y.mean(), 0)
ax.plot(x, y, **DATA_STYLE)
ax.plot(range(7), f, **MODEL_STYLE)
ax.set_xticks(range(7))
ax.set_xticklabels(weekdays)
return ax
def plot_weektrend(data, samples, ax=None):
dates = data["date"]
weekdays = ["Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun"]
y = data["births_relative"]
mean, sdev = y.mean(), y.std()
intercept = samples["intercept"][:, None]
f1 = samples["trend/f"]
f2 = samples["year/f"]
g3 = samples["week-trend/f"]
baseline = ((intercept + f1 + f2) * y.std()).mean(0)
if ax is None:
ax = plt.gca()
ax.plot(dates, y - baseline, **DATA_STYLE)
for n, day in enumerate(weekdays):
week_beta = samples["week/beta"][:, n][:, None]
fsd = jnp.exp(g3) * week_beta
f = jnp.quantile(fsd * sdev + mean, 0.50, axis=0)
ax.plot(dates, f, **MODEL_STYLE)
ax.text(dates.iloc[-1], f[-1], day)
return ax
def plot_1988(data, samples, ax=None):
indicators = get_floating_days_indicators(data["date"])
memorial_beta = samples["memorial/beta"][:, None]
labour_beta = samples["labour/beta"][:, None]
thanks_beta = samples["thanksgiving/beta"][:, None]
memorials = indicators["memorial_days_indicator"] * memorial_beta
labour = indicators["labour_days_indicator"] * labour_beta
thanksgiving = indicators["thanksgiving_days_indicator"] * thanks_beta
floating_days = memorials + labour + thanksgiving
is_1988 = data["date"].dt.year == 1988
days_in_1988 = data["day_of_year"][is_1988] - 1
days_effect = samples["day/beta"][:, days_in_1988.values]
floating_effect = floating_days[:, jnp.argwhere(is_1988.values).ravel()]
y = data["births_relative"]
f = (days_effect + floating_effect) * y.std() + y.mean()
f_median = jnp.median(f, axis=0)
special_days = {
"Valentine's": "1988-02-14",
"Leap day": "1988-02-29",
"Halloween": "1988-10-31",
"Christmas eve": "1988-12-24",
"Christmas day": "1988-12-25",
"New year": "1988-01-01",
"New year's eve": "1988-12-31",
"April 1st": "1988-04-01",
"Independence day": "1988-07-04",
"Labour day": "1988-09-05",
"Memorial day": "1988-05-30",
"Thanksgiving": "1988-11-24",
}
if ax is None:
ax = plt.gca()
ax.plot(days_in_1988, f_median, color="k", lw=2)
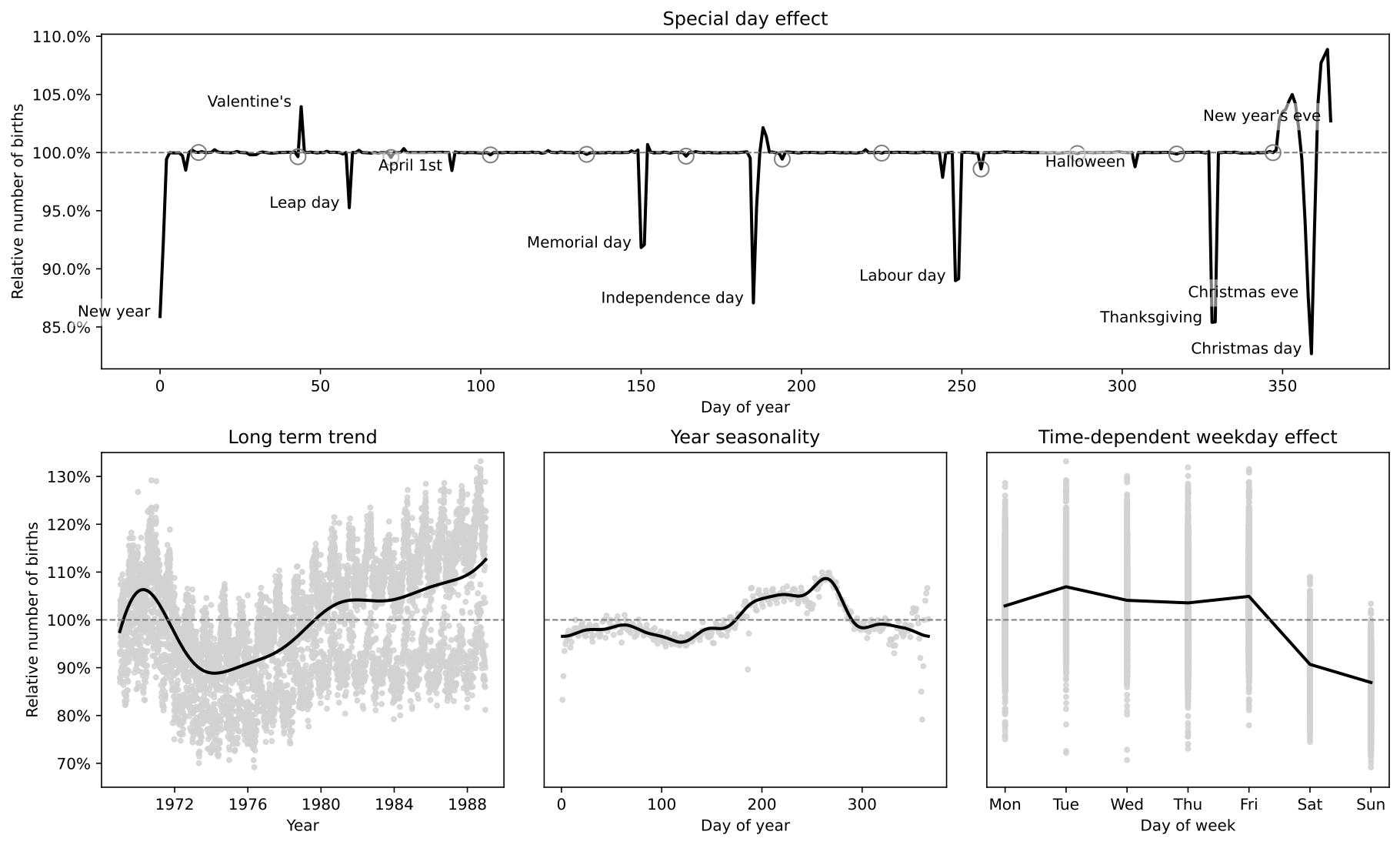
for name, date in special_days.items():
xs = pd.to_datetime(date).day_of_year - 1
ys = f_median[xs]
text = ax.text(xs - 3, ys, name, horizontalalignment="right")
text.set_bbox(dict(facecolor="white", alpha=0.5, edgecolor="none"))
is_day_13 = data["date"].dt.day == 13
bad_luck_days = data.loc[is_1988 & is_day_13, "day_of_year"] - 1
ax.plot(
bad_luck_days,
f_median[bad_luck_days.values],
marker="o",
mec="gray",
c="none",
ms=10,
lw=0,
)
return ax
def make_figure(data, samples):
import matplotlib.ticker as mtick
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 9))
grid = plt.GridSpec(2, 3, wspace=0.1, hspace=0.25)
axes = (
plt.subplot(grid[0, :]),
plt.subplot(grid[1, 0]),
plt.subplot(grid[1, 1]),
plt.subplot(grid[1, 2]),
)
plot_1988(data, samples, ax=axes[0])
plot_trend(data, samples, ax=axes[1])
plot_seasonality(data, samples, ax=axes[2])
plot_week(data, samples, ax=axes[3])
for ax in axes:
ax.axhline(y=1, linestyle="--", color="gray", lw=1)
if not ax.get_subplotspec().is_first_row():
ax.set_ylim(0.65, 1.35)
if not ax.get_subplotspec().is_first_col():
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.set_ylabel("")
else:
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(mtick.PercentFormatter(xmax=1))
ax.set_ylabel("Relative number of births")
axes[0].set_title("Special day effect")
axes[0].set_xlabel("Day of year")
axes[1].set_title("Long term trend")
axes[1].set_xlabel("Year")
axes[2].set_title("Year seasonality")
axes[2].set_xlabel("Day of year")
axes[3].set_title("Day of week effect")
axes[3].set_xlabel("Day of week")
return fig
# --- functions for running the model --- #
def parse_arguments():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Hilbert space approx for GPs")
parser.add_argument("--num-samples", nargs="?", default=1000, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--num-warmup", nargs="?", default=1000, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--num-chains", nargs="?", default=1, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--device", default="cpu", type=str, help='use "cpu" or "gpu".')
parser.add_argument("--x64", action="store_true", help="Enable double precision")
parser.add_argument(
"--save-figure",
default="",
type=str,
help="Path where to save the plot with matplotlib.",
)
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
def main(args):
is_sphinxbuild = "NUMPYRO_SPHINXBUILD" in os.environ
data = load_data()
data_dict = make_birthdays_data_dict(data)
mcmc = MCMC(
NUTS(birthdays_model, init_strategy=init_to_median),
num_warmup=args.num_warmup,
num_samples=args.num_samples,
num_chains=args.num_chains,
progress_bar=(not is_sphinxbuild),
)
mcmc.run(jax.random.PRNGKey(0), **data_dict)
if not is_sphinxbuild:
mcmc.print_summary()
if args.save_figure:
samples = mcmc.get_samples()
print(f"Saving figure at {args.save_figure}")
fig = make_figure(data, samples)
fig.savefig(args.save_figure)
plt.close()
return mcmc
if __name__ == "__main__":
assert numpyro.__version__.startswith("0.18.0")
args = parse_arguments()
numpyro.enable_x64(args.x64)
numpyro.set_platform(args.device)
numpyro.set_host_device_count(args.num_chains)
main(args)